Introduction:
In the vast theater of Earth's climate, El Niño and La Niña emerge as captivating protagonists, orchestrating a climatic ballet that spans the Pacific Ocean. These phenomena, known as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), play a pivotal role in shaping global weather patterns, influencing everything from droughts and floods to hurricanes and heatwaves. To comprehend the intricacies of El Niño and La Niña, we must embark on a journey into the heart of the Pacific, where these climate phenomena unfold.
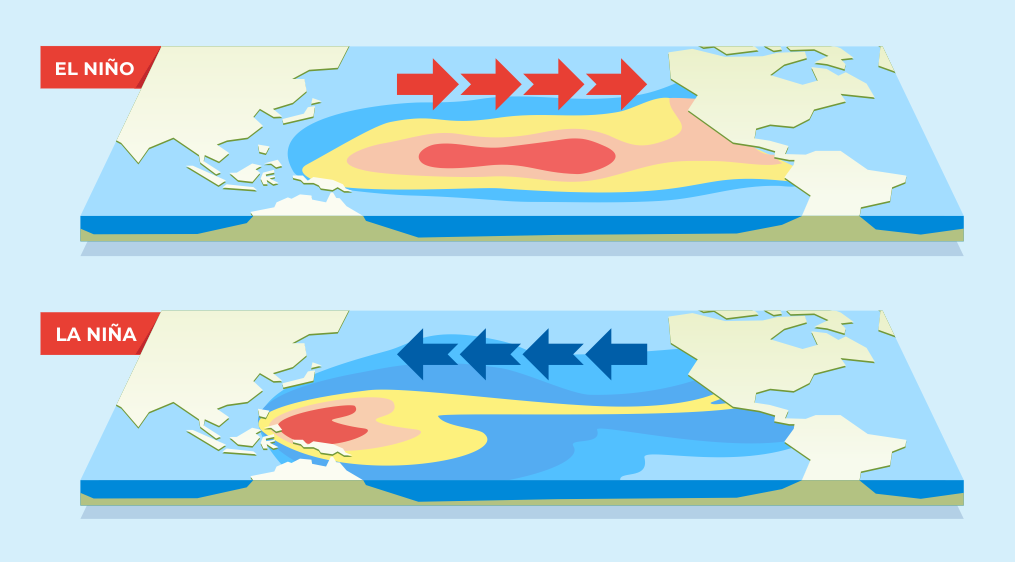
The Dance of El Niño:
El Niño, Spanish for "The Little Boy" or "Christ Child," is aptly named for its occurrence around Christmas time in the Pacific Ocean. At its core, El Niño is characterized by the abnormal warming of sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific. This warming disrupts the usual atmospheric circulation patterns, triggering a cascade of effects worldwide.
During El Niño, the normally easterly trade winds weaken, allowing warm waters to migrate eastward. This displacement of warm water alters atmospheric pressure, leading to the weakening of the Pacific Walker Circulation – a massive atmospheric circulation system over the equatorial Pacific. The consequences ripple across the globe, manifesting as increased rainfall in some regions, droughts in others, and more intense tropical cyclones.
Impacts of El Niño:
- Droughts and Heatwaves:
- El Niño often brings about prolonged periods of drought in regions such as Australia, Indonesia, and parts of Africa, leading to water shortages and agricultural challenges.
- Increased temperatures are observed globally, contributing to heatwaves in various parts of the world.
- Flooding and Storms:
- While some areas experience dry conditions, others face excessive rainfall and flooding. South America, for example, may witness heavy precipitation and increased river flows.
- Impact on Fisheries:
- The warming of Pacific waters affects marine ecosystems, disrupting fisheries and leading to changes in the distribution of marine species.
La Niña: The Antithesis of El Niño
In contrast to El Niño's warming tendencies, La Niña, or "The Little Girl" in Spanish, is characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific. This phenomenon intensifies the Pacific Walker Circulation, resulting in stronger easterly trade winds and upwelling of cold oceanic waters.
Effects of La Niña:
- Enhanced Hurricane Activity:
- La Niña is associated with increased hurricane activity in the Atlantic basin, posing heightened risks to coastal regions.
- Heavy Rainfall and Flooding:
- Certain areas experience above-average rainfall, leading to flooding in regions like Southeast Asia and Australia.
- Impact on Agriculture:
- La Niña tends to favor wetter conditions in some agricultural regions, benefiting crops. However, excessive rainfall can also lead to soil erosion and other challenges.
Balancing Act: The ENSO Cycle
The interplay between El Niño and La Niña creates a delicate dance known as the ENSO cycle. This cycle typically occurs every 2 to 7 years and has a profound impact on global climate variability. Understanding and predicting these phenomena are crucial for governments, meteorological agencies, and communities to prepare for and mitigate the potential impacts.
Predicting ENSO Events:
Meteorologists employ various tools and models to forecast ENSO events. One key indicator is the Southern Oscillation Index (SOI), which measures the difference in air pressure between Tahiti and Darwin, Australia. Additionally, sea surface temperature anomalies in the equatorial Pacific are closely monitored.
Conclusion:
El Niño and La Niña, the dynamic duo of the Earth's climate, weave a narrative of interconnectedness that transcends geographic boundaries. Their influence extends far beyond the Pacific, shaping weather patterns, affecting ecosystems, and impacting human societies across the globe. As we continue to grapple with the complexities of climate change, a deeper understanding of these phenomena becomes increasingly crucial for adapting to and mitigating the consequences of our ever-evolving climate.
Unraveling the Enigma of El Niño and La Niña: Nature's Dynamic Duo